Testing (2).png)
EMC/EMI testing is a critical step in the design and manufacturing processes of electronic devices. Various regulatory bodies, including the FDA, FCC, and ISO, have set specific limits on the emissions that can be released from an electronic device. These EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) regulations provide improved reliability and safety for anyone using electrical and electronic equipment because they assure the device does not interfere with the operation of other equipment or fail to operate as intended due to interference from others emissions. Failing to pass EMC compliance testing can result in fines and product recalls.
So purchasing instruments that can spot potential EMC/EMI issues prior to EMC testing is worth the investment. Though EMI and EMC are very similar, there are a few differences between the two.
Check out our EMC solutions page and learn the following:
- Take the mysteries out of EMI/EMC test setup
- Troubleshoot to speed up debug work
- Test to standards, and which standards Tek supports
- Compile a complete pre-compliance testing solution
What is EMI ?
|
Sometimes called radio frequency interference (RFI), electromagnetic interference (EMI) occurs when electromagnetic energy disrupts the operation of an electronic device. The source of EMI can be man-made, such as other electrical devices like switch-mode power supplies, personal computers, or naturally occurring, such as electrical storms, solar radiation, or even cosmic noises.
|
What is EMC? |
|
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device to operate as intended in an environment with other electrical devices or sources of EMI without affecting those other devices. A device is said to be EMC-compliant when it does not influence the electromagnetic environment to the extent that other devices and systems are negatively affected. |
What is EMI and EMC Testing?To ensure compliance with EMI and EMC national and international regulations, many companies employ the services of a specialized testing facility. Since these tests are expensive—even if the product fails—several companies perform EMC pre-compliance testing in-house. If they have a sophisticated enough lab, companies may also perform EMC compliance testing in-house.
IEMC/EMI testing is typically divided into two categories: immunity testing and emissions testing. |
|
Types of EMC tests |
|
|
When electronics are submitted to EMC testing labs, there are many types of EMC tests these labs run. Generally speaking, EMC testing is divided into two categories: immunity testing and emissions testing.
|
Emissions Testing
Emissions testing is the process of measuring the RF emissions – both radiated and conducted – of a DUT/EUT to determine if its emissions levels do not exceed the limits defined by the appropriate standard.
Radiated emissionsRadiated emissions are the intentional and unintentional release of electromagnetic energy from an electronic device. A radiated test is performed to ensure emissions emanating from the DUT or EUT comply with the applicable limits. |
Conducted emissionsConducted emissions are the coupling of electromagnetic energy from a device to its power cord. Like radiated emissions, the allowable conducted emissions from electronic devices are controlled by different regulatory agencies and testing is performed to ensure emission levels are below the applicable limits. |
EMC testing labs
EMC-compliance tests are commonly done off-site prior to the production of a device. Open-air test sites, or OATS, are the reference sites used for most standards. They are especially useful for emissions testing of large equipment systems. However, RF testing of a physical prototype is more often carried out indoors, in a specialized anechoic chamber. Types of chambers include anechoic, reverberation, and the gigahertz transverse electromagnetic cell (GTEM cell).
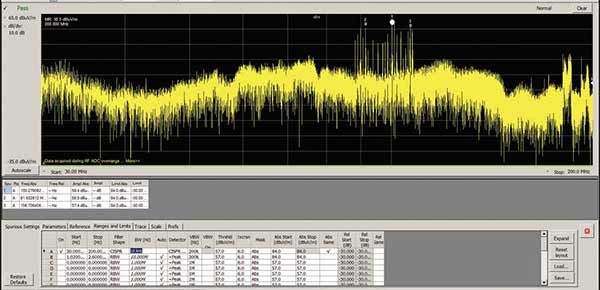
EMC testing procedure and average pass rate
Roughly 50 percent of products pass their first EMC compliance test when pre-compliance isn’t considered, so it’s essential to understand the process and standards a device is tested to in order to increase your chances of success.
EMC compliance testing can take up to two weeks to complete—not including the time it takes to get your product into the test queue—and can cost up to $20,000 per submission. A failure in EMC compliance can result in expensive redesigns and product launch delays. And since nearly 50 percent of products fail their first EMC compliance test when pre-compliance isn’t considered, it’s likely that you’ll need to repeat your visit to the test house, multiplying costs over time.Once a product has gone through pre-compliance testing and passed the test with a sufficient margin, it needs to be formally certified by an EMC testing lab. Accredited labs are the gold-standard for EMC testing and choosing an accredited lab is always recommended—though not necessary—to ensure your device is ready to go to market. There are, however, some instances that require certification from a NATA accredited lab, including devices that fall under the 'certification' authorization procedures.
How to pass EMC Compatibility testing
EMC pre-compliance testing is a fast and affordable way to ensure products pass EMC tests the first time In the early development stages, design-for-EMC techniques are combined with diagnostics to build products with low susceptibility to both external and internal interference. Later in the development cycle, pre-compliance testing is used to catch compliance problems and improve the probability of a successful first pass of full EMC-compliance testing.
Additional benefits of pre-compliance EMC testing, include:
- Detects errors early, fixing potential issues
- Lowers testing and design costs
- Projects become more agile
- Lowers risk of failure and leads to assured compliance
- Addresses both over and under design and engineering
For a better understanding of how a Tektronix pre-compliance testing setup compares to an EMC testing lab, watch this short video.
Setting up a pre-compliance test labWhen selecting a test site, rural areas, conference rooms, and basements are good options because they minimize external signals that might mask the DUT emission levels you are trying to measure. Other considerations for improving accuracy include having a good ground plane and reducing the number of reflective objects around the test area. Check out our comprehensive range of EMI/EMC Test Accessories in our webshop via the button below
|
EMI and EMC testing products
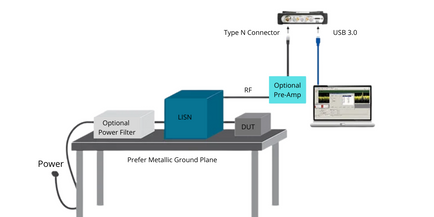
The goal of EMC pre-compliance testing is to mimic the compliance test set up within an acceptable margin to uncover potential problems and reduce risk of failure prior to the expensive compliance test. EMC pre-compliance testing typically involves:
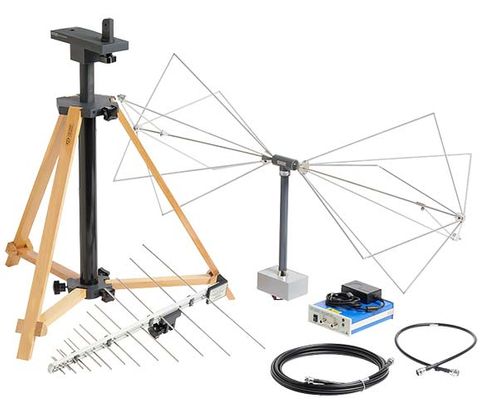
- Spectrum analyzer with quasi-peak detector
- Preamplifier (optional)
- Antenna with non-metallic stand for radiated emissions
- Line impedance stabilization network (LISN) for conducted test
- Power limiter for conducted test
- EMC near-field probes for diagnostics (optional)
- Oscilloscope with frequency and time correlation capabilities to assist in debugging (optional)
- EMC testing software

.png)